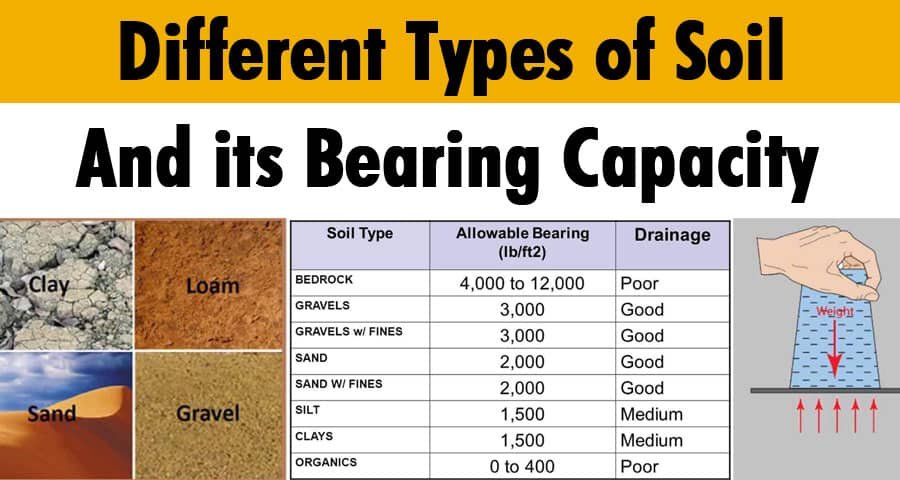
Soil is the foundation of every structure. Whether you’re building a house, bridge, highway, or dam, the strength of the soil determines the safety and stability of your structure.
The maximum bearing capacity of soil tells us how much load the ground can handle without failure or excessive settlement. Civil engineers in India rely on IS codes and on-site testing to calculate this value accurately.
In this detailed guide, we will cover definitions, formulas, methods, values, IS guidelines, FAQs, and examples to make this topic simple and exam-ready.
1. What is Bearing Capacity?
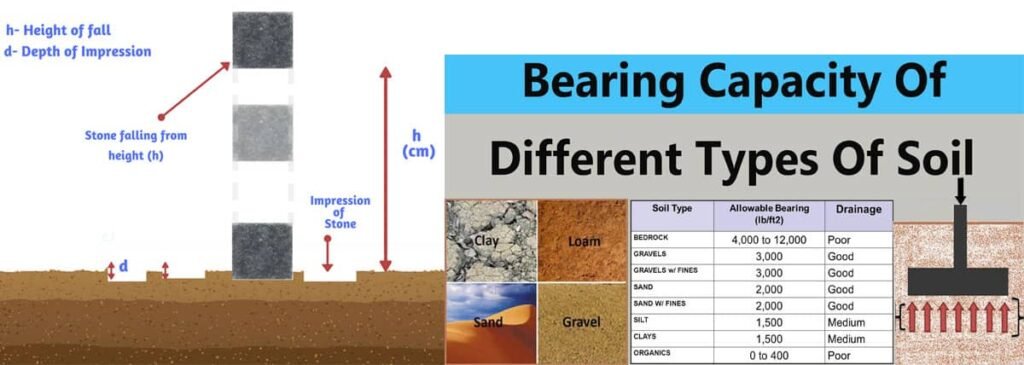
Bearing capacity is the maximum load per unit area that soil can safely withstand without experiencing failure or excessive settlement.
- Unit: Usually expressed in kN/m² or kg/cm².
- Key point: Exceeding this value may cause the structure to tilt, settle, or even collapse.
2. Importance of Bearing Capacity in Civil Engineering
Knowing the safe bearing capacity is essential for:
- Selecting shallow or deep foundations.
- Preventing structural damage.
- Designing economical foundations.
- Meeting IS code requirements.
- Ensuring long-term stability.
3. Types of Bearing Capacity
| Type | Definition | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Ultimate Bearing Capacity (qu) | Maximum load before soil failure. | Used in theory. |
| Net Ultimate Bearing Capacity (qun) | qu−γDfqu – \gamma D_fqu−γDf, subtracting overburden pressure. | Refines analysis. |
| Safe Bearing Capacity (qs) | Allowable load considering a factor of safety. | Used for design. |
4. Factors Affecting Bearing Capacity
| Factor | Effect on Bearing Capacity |
|---|---|
| Type of soil | Rocks > Gravels > Sands > Silts > Clays. |
| Moisture | Higher water content reduces strength. |
| Density | Denser soils provide higher capacity. |
| Foundation depth | Deeper footings usually have higher values. |
| Water table | High water table reduces effective strength. |
| Footing shape | Circular footings distribute loads better. |
| Load inclination | Inclined loads reduce effective capacity. |
Also Read Civil Engineering Interview Questions and Answers
5. Typical Soil Bearing Capacity Values in India
| Type of Soil | Safe Bearing Capacity (kN/m²) | Safe Bearing Capacity (kg/cm²) |
|---|---|---|
| Soft clay | 50 – 75 | 0.5 – 0.75 |
| Medium clay | 100 – 150 | 1.0 – 1.5 |
| Dense sand | 250 – 450 | 2.5 – 4.5 |
| Loose sand | 100 – 150 | 1.0 – 1.5 |
| Gravel | 300 – 600 | 3.0 – 6.0 |
| Soft rock | 450 – 900 | 4.5 – 9.0 |
| Hard rock | 1000 – 3000 | 10 – 30 |
Tip for Exams: These approximate values are frequently asked in SSC JE, RRB JE, and GATE.
6. Methods of Determining Bearing Capacity
6.1 Terzaghi’s Method
Formula:
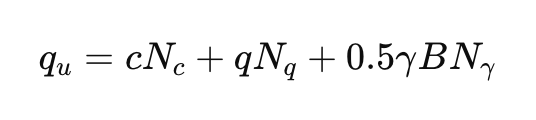
Where:

6.2 Meyerhof’s Theory
Enhances Terzaghi’s formula by considering:
- Footing shape
- Depth
- Load inclination
6.3 IS 6403:1981 Guidelines
The Indian Standard Code provides:
- Recommended safe bearing capacities.
- Design charts for different soil types.
- Factors of safety based on foundation type.
6.4 Plate Load Test
Steps:
- Place a steel plate at foundation depth.
- Apply incremental loads using a hydraulic jack.
- Record settlements at each stage.
- Calculate safe bearing capacity from the load-settlement curve.
6.5 Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
- A split-spoon sampler is driven into soil using a hammer.
- Count the number of blows needed for a 30 cm penetration.
- Use the N-value in empirical formulas to estimate capacity.
6.6 Cone Penetration Test (CPT)
- Push a cone-shaped probe into the soil at a constant rate.
- Measure resistance directly.
- Best suited for sandy and silty soils.
Example Calculation
Given:
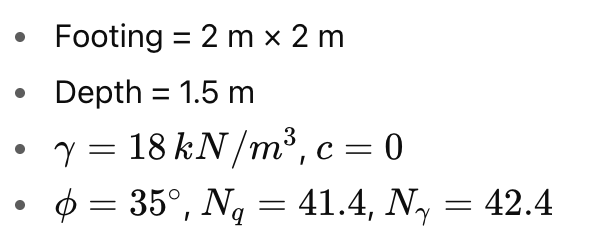
Step 1: Calculate overburden pressure.
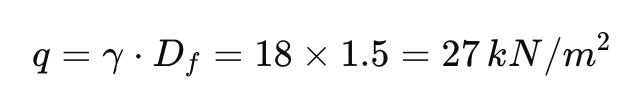
Step 2: Apply Terzaghi’s formula.
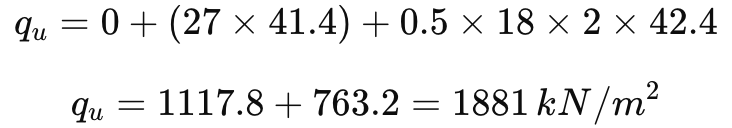
Step 3: Safe bearing capacity:
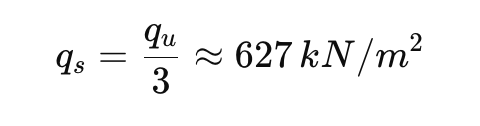
Safe vs. Ultimate Bearing Capacity
| Aspect | Ultimate Bearing Capacity | Safe Bearing Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | quq_uqu | qsq_sqs |
| Definition | Maximum pressure before failure | Allowable pressure with FOS |
| Factor of Safety | Not included | Included |
| Application | Theoretical analysis | Practical foundation design |
Applications in Foundation Design
- Selection of isolated, combined, or raft footings.
- Deciding between shallow and deep foundations.
- Designing pile foundations in weak soils.
- Avoiding settlement and structural instability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the maximum bearing capacity of soil in India?
Hard rock: 1000–3000 kN/m²
Dense sand/gravel: 300–600 kN/m²
Soft clay: 50–75 kN/m²
Q2. Which IS code is used for soil bearing capacity?
IS 6403:1981 — Code of practice for foundation design.
Q3. What are common on-site tests?
Plate load test
Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
Cone Penetration Test (CPT)
Q4. What is the usual factor of safety?
Typically 2.5 to 3 for shallow foundations.
Q5. Is this topic important for civil exams?
Absolutely. Frequently asked in SSC JE, RRB JE, GATE, and State PSCs.
Conclusion
The maximum bearing capacity of soil is a fundamental concept in civil engineering. It helps engineers design safe, cost-effective, and durable foundations. In India, where soil properties vary widely, following IS 6403 guidelines and conducting on-site tests is essential.
A solid understanding of this topic ensures safer structures and better-performing infrastructure.