Introduction
In reinforced cement concrete (RCC) design, two main approaches are used: Working Stress Method (WSM) and Limit State Method (LSM).
Both methods have been widely used in civil engineering for structural design.
While the Working Stress Method is based on elastic theory and was popular in the past, the Limit State Method is the modern approach adopted in most Indian Standard (IS) codes.
Understanding the difference between Working Stress Method and Limit State Method is important for engineers, students, and construction professionals.
This article explains each method in detail, compares them, highlights their advantages, disadvantages, and practical applications.
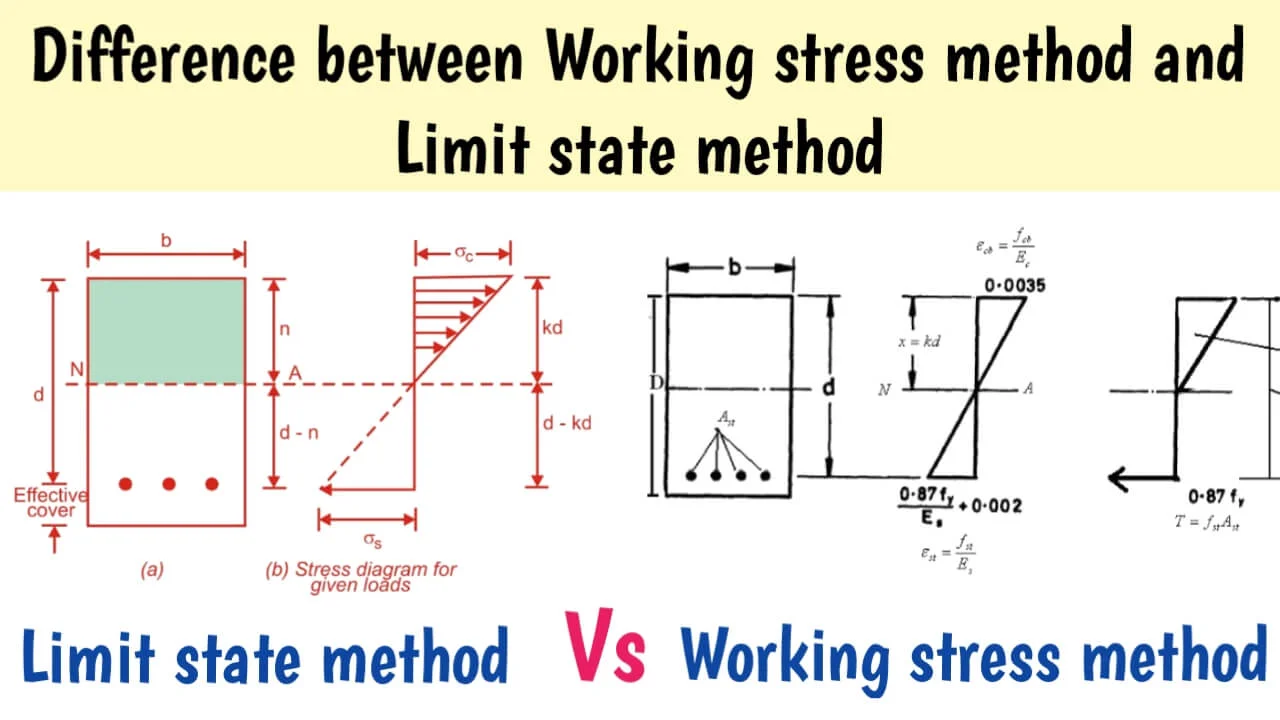
What is the Working Stress Method (WSM)?
The Working Stress Method is the traditional method for RCC design.
It is based on the elastic theory, where materials are assumed to behave elastically up to their permissible stress.
- Design Philosophy: Structures are designed so that the stresses in materials do not exceed their permissible limits under service loads.
- Safety: Safety is ensured by applying a factor of safety to the yield stress of the material.
- Serviceability: High level of serviceability since deformations and cracks are minimized.
Key Characteristics of WSM
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Basis | Elastic theory |
| Factor of Safety | Applied to material yield stress |
| Stress Distribution | Assumed linear |
| Safety Consideration | Against collapse |
| Serviceability | Excellent |
| IS Code Reference | IS 456:2000 (earlier practice) |
What is the Limit State Method (LSM)?
The Limit State Method is the modern approach recommended in IS 456:2000 for RCC design.
It ensures both safety and serviceability under different loading conditions.
- Design Philosophy: Structures are designed to withstand ultimate loads without collapse and to remain functional during service life.
- Safety Factors: Partial safety factors are applied to both loads and material strengths.
- Economic Design: More economical compared to WSM as it allows better utilization of material strength.
Key Characteristics of LSM
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Basis | Ultimate load theory |
| Safety Factors | Applied separately to loads and material strengths |
| Stress-Strain Relationship | Non-linear |
| Safety Consideration | Against collapse and serviceability failures |
| Serviceability | Good, but not as conservative as WSM |
| IS Code Reference | IS 456:2000 (current practice) |
Difference Between Working Stress Method and Limit State Method
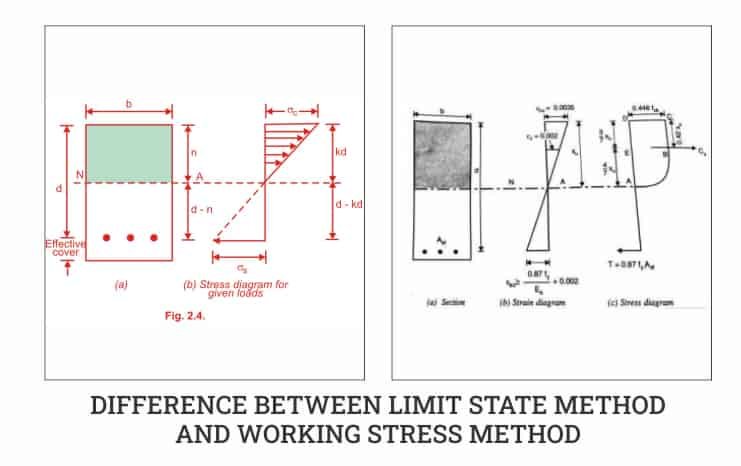
Below is a detailed comparison table:
| Aspect | Working Stress Method (WSM) | Limit State Method (LSM) |
|---|---|---|
| Basis | Elastic theory | Ultimate load theory |
| Stress Distribution | Linear | Non-linear |
| Factor of Safety | Applied on material strength | Partial safety factors applied to both loads and strengths |
| Economy | Less economical | More economical |
| Serviceability | Excellent | Adequate |
| Load Consideration | Service loads only | Ultimate and service loads |
| Adoption in India | Outdated in practice | Recommended in IS codes |
| Material Utilization | Less efficient | Efficient utilization |
Also Read Slip Formwork in Construction: Fast, Seamless & Modern Concrete Casting
Advantages of Working Stress Method
- Very simple to understand and apply.
- Conservative approach ensures high serviceability.
- Good for structures where deflection and cracking must be minimized.
Disadvantages of Working Stress Method
- Uneconomical use of materials.
- Does not consider actual ultimate load capacity.
- Outdated for modern high-strength materials.
Advantages of Limit State Method
- Ensures both safety and serviceability.
- Economical design due to better material utilization.
- Allows consideration of different load combinations.
- Recommended by IS 456:2000 and widely used globally.
Disadvantages of Limit State Method
- Slightly more complex in calculations.
- Serviceability criteria may not be as conservative as WSM.
Applications in Construction
- Working Stress Method: Still used for water-retaining structures, small residential works, and masonry design.
- Limit State Method: Used for high-rise buildings, bridges, industrial structures, and all major RCC projects in India.
Example Calculation – Flexural Design in WSM vs LSM
To better understand the difference, let’s take a simple beam design scenario:
| Parameter | WSM Calculation | LSM Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Load Consideration | Service load | Ultimate load |
| Factor of Safety | Higher | Lower |
| Steel Requirement | More | Less |
| Result | Safer but uneconomical | Economical with adequate safety |
IS Code Recommendations
- IS 456:2000 recommends Limit State Method for RCC design.
- Working Stress Method is only retained for special cases like water tanks (IS 3370).
Conclusion
Both Working Stress Method and Limit State Method have their place in RCC design.
While WSM is more conservative and ensures excellent serviceability, LSM provides an economical and safe design that meets modern construction needs.
In India, the Limit State Method is the standard for most structures as per IS codes.
However, engineers should understand both methods for academic, practical, and professional purposes.
FAQs
Q1. Which method is used in IS 456:2000 for RCC design?
The Limit State Method is recommended, while WSM is retained for special cases.
Q2. Why is Limit State Method more economical?
The Limit State Method is recommended, while WSM is retained for special cases.
It allows better material utilization and considers actual load capacity.
Q3. Is Working Stress Method outdated?
Yes, for most RCC works, but still used in special structures like water tanks.
Q4. Which method is better for serviceability?
Working Stress Method is more conservative for deflection and crack control.